Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment Disposal (WEEE)
Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment Disposal Introduction
Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment or commonly abbreviated as WEEE, refers to electrical and electronic equipment that’s nearing its end of life or is no longer useful. Equipment that falls under the WEEE waste category includes mobile phones, desktop computers, laptops, servers, televisions, kitchen appliances, printers, and any other electrical equipment at the end of its life. WEEE waste disposal is governed by laws and regulations to prevent toxic materials from harming human beings and animals. If not properly regulated, WEEE disposal can cause environmental disasters such as soil and water contamination, diseases, and poor air quality. Companies such as TechReset and secure WEEE recycling Ltd have created voluntary WEEE disposal initiatives to manage waste and provide job opportunities.
What is Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment

WEEE waste disposal covers any item that has a plug and/or battery. These items are considered electrical and electronic equipment. WEEE disposal from electric and electronic equipment ranges from IT devices, Home equipment to large-scale manufacturing electronics. How do you decide if the equipment is waste?
- If you cannot utilize it for its original purpose, i.e., it’s broken, outdated, or has malfunctioned.
- If you no longer use it regularly and it does not add value to your life or business.
- If it’s a burden to the user and there’s little incentive to keep it.

Make an Informed Decision
Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment Disposal (WEEE) Statistics
Statistics paint a grim picture of Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment. According to the Global E-waste Monitor 2020 report. The report is a collaborative effort between various international bodies that estimated 53.6 million metric tonnes of e-waste was generated across the world in 2019. This weight was the equivalent of 350 Queen Mary II-sized cruise ships and was a 20% increase from 2014.
Canada generates approximately 757 kilotonnes of WEEE per year with an e-waste collection rate of only 14%.
This amount of waste has had an adverse effect on the environment too. Hazardous materials from WEEE comprises 2.2 metric tonnes of lead glass, 0.3 metric tonnes of battery residue, and four kilotonnes of CFCs (Ozone-depleting materials).
Despite global efforts to reduce product usage and recycle waste, only 17.4% of WEEE is recycled, and 80% of documented e-waste is not being collected and recycled safely.
On the other hand, WEEE has created massive economic opportunities. It’s estimated that WEEE disposal and management is projected to grow into a $102 Billion market by 2027. This expansion is due to the growth of mobile technology and the reduced average life of electronic equipment.
From the statistics above, the rate of recycling WEEE is much lower than what’s being produced. This scenario presents both a problem for the environment and an opportunity for e-waste management companies to fill the unmet need.
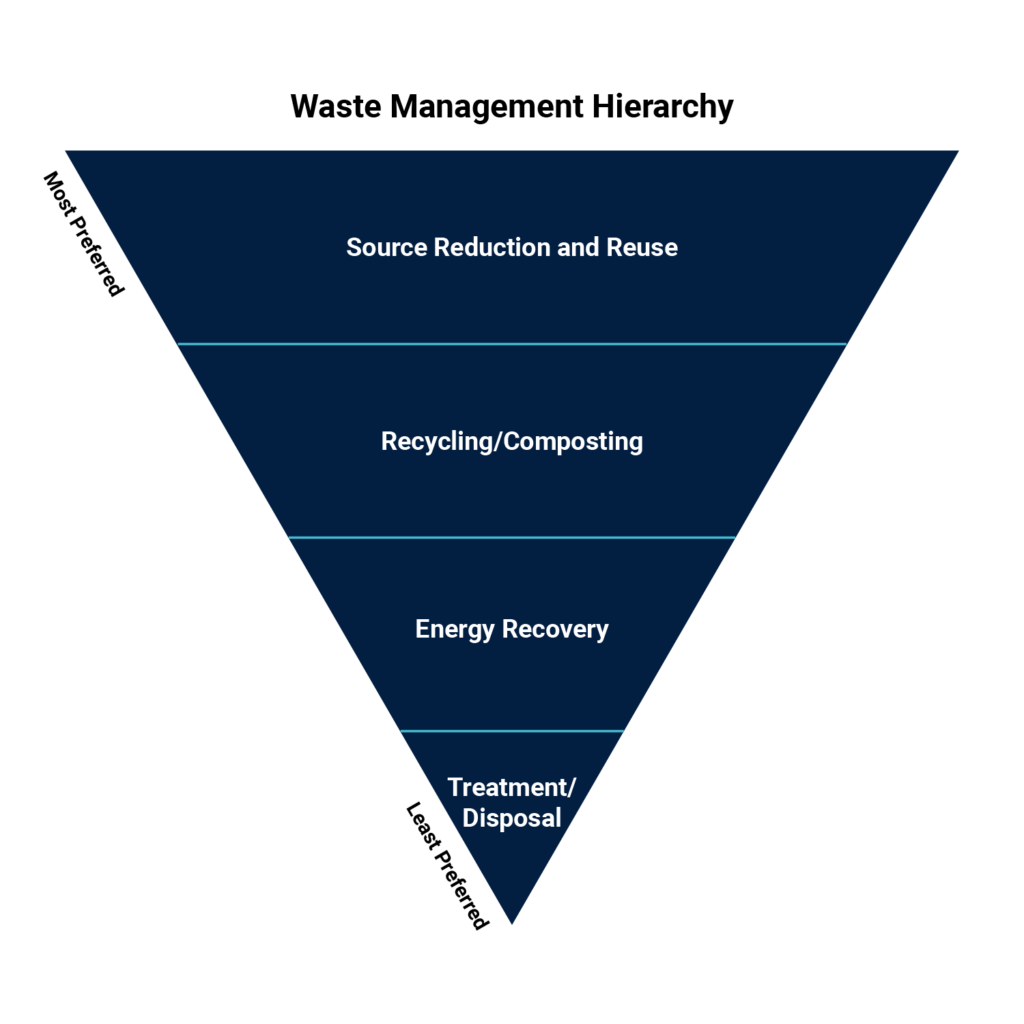
Waste Management Hierarchy for WEEE Disposal
The waste management hierarchy ranks WEEE disposal options according to the safest option for the environment. The first step promotes the reduction of waste. Manufacturers are encouraged to use less hazardous materials and design products that last longer. At the bottom of the hierarchy is the disposal option. Consumers and manufacturers should explore safer and environmentally sound options before disposing of waste through landfills and incineration.

See how much your IT equipment is worth
Secure WEEE Disposal Regulations
WEEE disposal companies and clients need to understand legislation and the WEEE regulations that govern WEEE waste disposal. These will inform the choice of e-waste disposal company you select for your business. From 2003 – 2010 Canadian provinces passed a series of e-waste management legislation.
The Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME) endorsed principles that govern WEEE waste disposal. These principles provide guidelines for setting up WEEE disposal programs that also protect the environment.
These principles are summarized as follows:
- WEEE waste disposal is the responsibility of the product manufacturer.
- The cost of managing WEEE programs will not be paid for by general taxpayers.
- Minimize the Impact on human health and the environment throughout the product manufacturing and disposal cycle.
- WEEE waste disposal should be consistent with the 4R’s of waste management, i.e., reducing, reusing, recycling, and recovering.
- Consumers of these products access (within reason) systems of collecting waste without being charged.
- Public authorities should educate consumers and relevant stakeholders on e-waste programs and how they can individually contribute to e-waste management.
- WEEE program design should aim for consistency and equity for consumers. The program design should accommodate consumers living in rural, remote, and urban areas.
- WEEE programs should include historical, orphan, residential, and commercial products.
- WEEE programs should provide reports on their performance and strive for financial management transparency.
- WEEE disposal should maximize social and economic benefits in a logistically feasible manner
- E-waste exports from Canada will only happen if recycling facilities have demonstrated their commitment to fair labor practices and environmentally sound management.
The Ontario Government released a Made-in-Ontario Environment Plan to govern how producers manage waste released from their products, production process, and packaging. The plan encourages producers to develop innovative, environmentally safe, and cost-effective ways to recycle WEEE while lowering the cost to consumers.

Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment Disposal (WEEE) Product Categories
Knowing WEEE product categories will help you select your ideal waste disposal company. Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment is classified into several categories as follows:
IT equipment
Items under this category include – Desktop computers, servers, laptops, smartphones, mobile phones, photocopy machines, printers, storage devices. IT equipment is disposed of through repurposing old equipment into usable condition, refurbishing, and reselling. This prevents e-waste from going into landfills. For storage devices, data is erased, degaussed, and hard drives are shredded.
Entertainment equipment
These include radios, TVs, Speakers, TV remotes, headsets, earphones. Since these devices do not store data, they are refurbished and resold. These items are also recycled and parts reused to manufacture more equipment. If they are no longer functional, the equipment is shredded and incinerated.
Large and small household appliances
Appliances in this category include washing machines, freezers, refrigerators, dishwashers, hairdryers, coffee machines, toasters, irons. The discarded waste is collected and transported to a recycling plant. Here, the waste is sorted to recover usable parts for manufacturing end products. The remaining waste is taken through shredding mills. The shredded and recycled parts are repurposed into plastics and metal that can be reused.
Medical equipment
Medical equipment is recycled differently due to its sensitivity. Only verified re-processors are allowed to dispose of medical equipment to prevent cross-contamination. For single-use items, they undergo cleaning, sterilization, and inspection. Reprocessing medical equipment helps hospitals reduce waste and cut the costs of repurchasing new items.
Lighting equipment
These include LED bulbs, fluorescent bulbs, and lighting cables. Lighting fixtures contain materials such as copper, glass, aluminum, recyclable plastics. These items are collected and sorted in a recycling facility.
Other waste product categories that use similar recycling processes as explained above include:
- Automated dispensers such as water dispensers, medical dispensers.
- Monitoring equipment such as security cameras, scanning equipment, smoke detection equipment.
- Electrical tools such as electronic drills, power saws, screwdrivers, handheld woodcutters, sewing machines.
- Leisure equipment and toys such as electrical toys for children, power gym items.
Common Hazardous Material Found in Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment
WEEE contains hazardous materials and chemicals that are toxic to human beings and animals. Proper disposal of these materials is critical to protecting the environment.
Lead
Lead is a component used to manufacture glass panels and gaskets in computers. Lead is also used for soldering in circuit boards. Though improvements in manufacturing have decreased the toxicity levels of lead in computer materials, high amounts of lead in the body cause damage to the nervous system, kidneys, and reproductive system.
Mercury
Mercury is used on printed circuit boards, thermostats, measuring equipment, medical equipment, mobile phone batteries. When e-waste is not disposed of properly, mercury seeps through soil and water, contaminating crops and wildlife. Mercury can cause brain and kidney damage in animals and human beings.
Plastics
PVC (Poly-Vinyl Chloride) is a form of plastic used to manufacture cabling, computer hardware, and electronic casings. When plastics are incinerated without proper safety standards, harmful toxins are released, causing respiratory and reproductive problems in animals and people.
Cadmium
Cadmium levels in the environment are generally low; however, levels are increasing due to increased disposal of WEEE. Cadmium is classified as a carcinogen that causes irreversible complications to the skeletal and respiratory systems. Interventions have been implemented across the globe to reduce the amount of Cadmium released to the environment. Infra-red detectors, semiconductor chips, and chip resistors contain low levels of Cadmium.
Brominated Flame Retardants
BFRs are commonly used in the plastics, electronic, electric, and textile industries to reduce flammability in these products. BFR in electronics and electrical equipment mostly contains a compound called tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA). This compound has been found in soil, water, and the atmosphere and contributes to environmental pollution. TBBPA can accumulate in human beings through water and food consumed. Various studies have suggested that TBBPA is toxic to human beings and can compromise the immune system.
Toners
Cartridges containing toners are one of the common e-waste collected in landfills. Toners are used in printers and copier machines. Carbon Black is the main component in black toners. This ingredient in toners has been classified as a possible carcinogen to human beings. According to a study conducted by West Virginia University, microscopic nanoparticles in toners may change genetic profiles in human beings.
WEEE Waste Disposal Process
The WEEE waste disposal process can be broken down into three steps.
Step 1: WEEE Collection and Transportation
The disposal process starts with collection and transportation to the recycling plant. TechReset and Secure WEEE recycling Ltd have specialized collection trucks that visit your premises to collect e-waste. Both parties should witness the collection to ensure only approved materials are transported to the recycling plant.


Step 2: Shredding, Sorting, and Separation
The materials collected are sorted to separate reusable parts from waste. These parts are reprocessed into plastics and metal for manufacturing end products. Plastics are sorted with infra light or separation by density: Eddy currents and magnets sort metals such as steel and aluminum.
The remaining waste is shredded using hammer mills or incinerated. For sensitive equipment such as storage devices, the client can have them shredded on-site for security purposes.
Step 3: Reporting
The client receives a detailed report from the WEEE disposal company after completing the disposal process. This report indicates materials recycled, recovered spare parts, and items scheduled for resale. The report also states if the recycling was as per the WEEE regulations. A certificate of destruction is then issued to certify the process.
TechReset is among the companies leading WEEE disposal programs in Canada. Our nationwide reach ensures we dispose of waste according to provincial regulations while minimizing waste in landfills. We also help you calculate the return on investment from reselling refurbished electrical and electronic equipment with our ROI calculator. Our WEEE disposal is ISO certified and adheres to the R2 standards of recycling e-waste. For more information on how we can help you dispose of your e-waste in an environmentally friendly manner, contact us today.

See how we can solve your hard drive destruction needs
Related Posts

International E-Waste Day On October 14th – An Awareness Initiative
International E-Waste Day was introduced by the WEEE Forum in 2018 to encourage consumers for responsible and safe e-waste disposal. TechReset processes consumer devices as
Why Is E-Waste Mainly Concerning?
E-waste is amongst the most noteworthy contributors to the global landfill issue, as just a 5th of electronic devices are recycled. Moreover, electronic products have

Proper Storing & Staging Of IT Assets For Disposal
IT assets can quickly become a serious liability if they aren’t properly processed at end-of-life. Data breaches in Canada and the United States are mounting